The Process: Heuristic Evaluation
The team’s overall consensus was that a heuristic evaluation would provide the desired insights. So, a team of three evaluators analyzed the site using Jakob Nielsen’s set of heuristics. Each evaluator identified issues and made recommendations for solving them.
Our Observations and Findings
The findings that we reported to the client identified issues with navigation, findability, error handling, content hierarchy, page layout, and task flow. Our report documented specific problem areas, proposed solutions for them, and suggested priorities for implementing solutions. Our recommendations were as follows:
- navigation—A more clearly defined layout and information hierarchy would improve customers’ understanding of how to fulfill their objectives on the Web site. Plus, the information taxonomy might consider means of inviting user-generated content. This could promote interaction and content generation across the Web site. The layout hierarchy would be more effective if important pieces of information were on the home page.
- interaction—Users expect navigation bars to be consistent across a Web site. Therefore, tabs and menus should not disappear, then reappear as customers progress along their user journey. It is important to reduce users’ cognitive load by making information easily available. Providing appropriate feedback is essential to improving the user journey, including breadcrumbs, changing the color of a link once a user has clicked it, and the scent of information.
- content—Labels, content, and lists need to be clear and descriptive. On the client’s Web site the labels of tabs did not clearly describe their function or destination. Page titles and subtitles must clearly describe the content to motivate customers to read further. Inconsistencies in font styles and sizes should be eliminated.
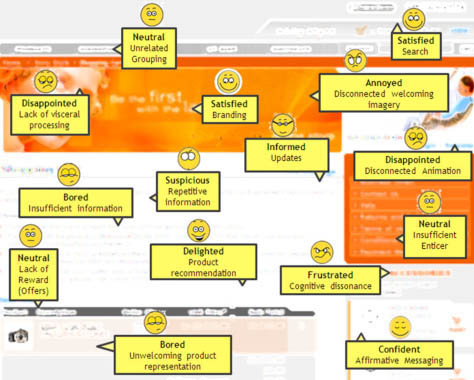
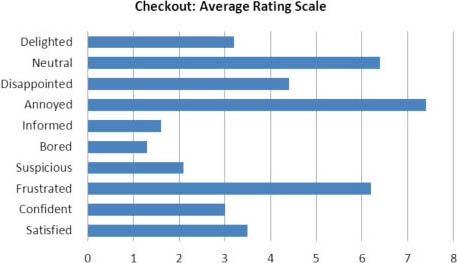
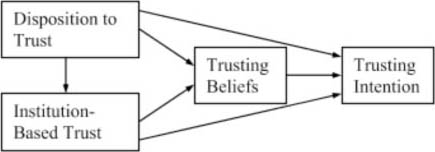
Although our heuristic evaluation provided an in-depth qualitative and quantitative analysis of the Web site’s task flows and interactions, heuristics failed to gauge customers’ satisfaction with the checkout experience. So, we followed up our heuristic evaluation with some usability testing to measure customers’ motivation and better understand other subjective factors like efficiency and satisfaction. However, these measures were limited to the ecommerce checkout system itself and did not take into account extraneous variables such as experience, privacy, motivation, or trust, shown in Figure 1.
Note—While various researchers differ on their understanding of trust, Kee and Knox considered a set of five factors: dispositional factors, situational factors, perceptions of the other, subjective trust, and behavioral trust.
A Critical Analysis of Our Method
From the evaluators’ critical analysis of our heuristic evaluation method, it became evident that this method did not result in a complete set of formal guidelines for a holistic checkout process that would lead to a satisfying user journey. One possible way of addressing this deficiency would have been to create a framework for documenting and addressing the issues that we identified. When evaluators come together to propose their recommendations for solutions, formal guidelines can help in suggesting improvements and prioritizing recommendations. From our analysis, we derived the quantitative scorecard shown in Figure 2.
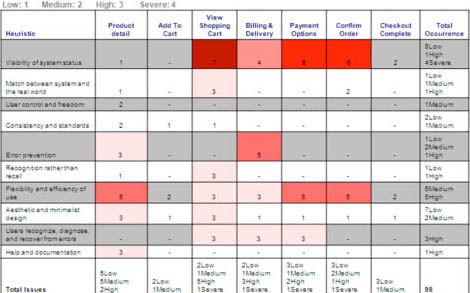
Although our formal assessment drove home some points, it failed to track issues relating to some essential factors of an ecommerce experience. For example, the report that we delivered failed to address any subjective factors of the checkout system’s customer experience. An evaluation scheme should address both subjective and objective heuristics for a system. It is also important to validate designs from an experiential perspective.
Advantages and Disadvantages
We identified the following advantages and disadvantages of the heuristic evaluation process.
- Advantages:
- objective—The results of a heuristic evaluation are structured objectively and well defined.
- collaborative—Several evaluators can come together to provide recommendations that the evaluators and the business can later prioritize.
- well structured—Heuristic evaluation is a formal process with clear, structured guidelines by which each evaluator can assess a product or service.
- prioritized—Critical issues come to the fore.
- Disadvantages:
- disparate findings—Several different evaluators may propose findings that differ from one another.
- lack of measurement—It is not possible to measure customer satisfaction, and task analysis does not reflect a keystroke model.
- limited to the software system—This method does not address extrinsic factors.